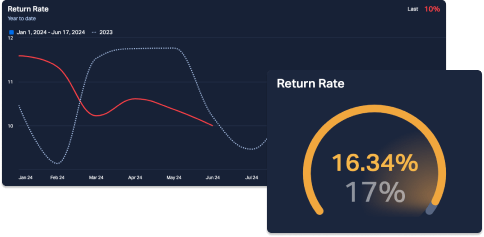
Rate of Return (RoR), also called Return on Investment (ROI) compares an investment to its gain or loss over time, expressed as a percentage of the original investment. A positive RoR indicates the investment has increased; a negative RoR indicates the investment has lost value.
Investments can consist of any number of assets, including but not limited to stocks, bonds, real estate, and fine art.
Rate of Return for your company’s assets is an important KPI for your finance team to monitor.